Overview
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) uses the physical principles of electromagnetic waves’ propagation throughout the media. The GPR transmitted signal will be reflected, refracted and diffracted from the boundaries between objects with different dieletric properties.
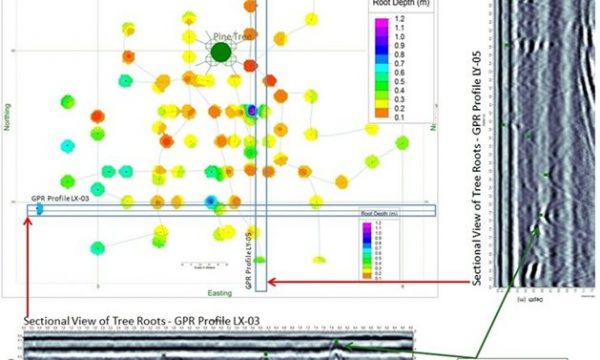
Root detection and mapping using GPR is possible due to the elevated moisture content of tree roots, which provides an excellent dielectric contrast with the soil matrix.

Survey grids are established over each work area allowing for accurate data collection, and an appropriate frequency of Ground Penetrating Radar is selected. GPS data are collected during the ground penetrating radar survey to allow for georeferenced data points and mapping software importing. Site photos are collected for tree species determination, grading and other site specific elements required for project interpretation.
Advantages
- Capable of scanning root systems of large trees in a relatively short time.
- Completely non-invasive – does not disturb soils or damage trees examined.
- Effective for monitoring root system development over time.
- Effective for scanning roots systems beneath concrete, asphalt, bricks, pavers and other hard surfaces.
- Capable of detecting roots with diametres as small as 1 centimetre.
Limitations
- Difficult to determine individual root size due to similarity in reflected signal display.
- Difficult to distinguish root ownership when imaging trees in close proximity.